
IP NEWS IN JAPAN
Outline Of The Recent Japanese Patent Law Revisions
Effective as of January 1, 1999
1. DAMAGE COMPENSATION FOR PATENT INFRINGEMENT
a. Formerly, damages have been calculated based on the usual or normal license royalty. Under the revised law, damages will be calculated by multiplying the number of the infringer’s products sold by the amount of profit the patentee should have obtained on each of these sales. This revision has raised the amount of compensatory damages that can be retrieved by patentees.(Japanese Patent Law – Article 102) b.The upper limit on fines levied for patent infringement by corporate entities has been raised to 150 million yen from 5 million yen.(Article 201)
2. PRIOR-FILING STATUS LIMITED
Patent applications and utility model applications which have been abandoned, withdrawn or subjected to a decision of final rejection shall be deemed never to have existed and will loose their prior-filing status against subsequent applications.(Article 39)
3. CLAIMING PRIORITY BASED ON EPC APPLICATIONS
Filings to Japan claiming priority from an EPC application will no longer require submission of an EPO priority certificate. This revision is a result of the establishment of an information exchange system between the JPO and the EPO.
Effective as of June 1, 1999
FEES OF REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION AND ANNUAL FEES
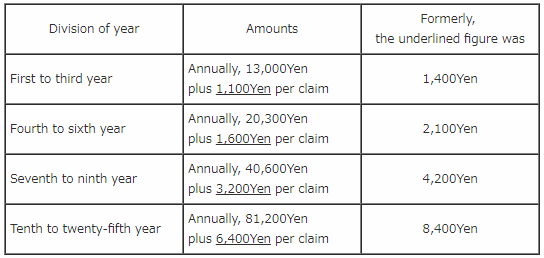
In fees of request for examination and annuities, the additional official fees for each additional claim added to a basic claim were reduced.(Articles 107 and 195) a.Fees of Request for examination 84,300Yen plus 2,000Yen per claim (Formerly, the underlined figure was 2,700Yen) b.Annuities
Effective as of January 1, 2000
1. INTRODUCTION OF EARLY LAYING OPEN OF A PATENT APPLICATION UPON APPLICANT'S REQUEST
Upon the applicant’s request, a patent application may be laid open to public inspection even before elapse of 1 year and 6 months after filing of the application. (Article 64 bis) (The applicant may thus make earlier an initial date for requesting the compensation payment against an infringer.)
2. REVISED REQUIREMENTS FOR PATENTABILITY
a. Inventions publicly known or publicly worked in a foreign country as well as in Japan prior to the filing of the patent application shall not be entitled to a patent.(Article 29-1-1,2)(“in a foreign country” is added.)
b. Inventions which could have been publicly available in a foreign country as well as in Japan via electronic telecommunication lines such as the internet, etc. prior to the filing of the application will not be entitled to a patent.(Article 29-1-3)
c.Inventions presented via electronic telecommunication lines can enjoy “exceptions to lack of novelty of invention”.(Article 30)
3. STIFFER PENALTIES FOR FRAUDULENT ACTS AND FALSE INDICATIONS
The maximum penalty for corporate entities for fraud and false indications will be raised to 100 million Yen from 3 million Yen.(Article 201)
4. REVISED CONDITIONS FOR APPLYING TO REGISTER AN EXTENSION OF THE TERM OF A PATENT
The requirement, as a condition for applying to extend the term of a patent, that legal requirements for safety or other considerations prevented the working of the patent(regarding e.g. medicine) for a certain minimum time period(i.e., at least 2 years) will be abolished.(Article 67)
Effective as of October 1, 2001
SHORTENED PERIOD OF REQUESTING FOR EXAMINATION OF A PATENT APPLICATION
The time period for submitting a request for examination of an application will be shortened to 3 years from the date of filing of the patent application, down from the current 7 years.(Article 48 ter) (This revised Article 48 ter. will be applied to applications filed on or after October 1, 2001)


